Development Notes¶
To install a local clone of the repository (for development):
git clone https://gitlab.com/rodrigomelo9/pyfpga.git
cd pyfpga
sudo pip install -e .
Note
With -e (–editable) your application is installed into site-packages via a kind of symlink, so you do not need to reinstall it after changes.
PyFPGA uses PEP8 guidelines.
The following is an overview of the main PyFPGA components and its relationship, which is explained in the sub-sections of this document.
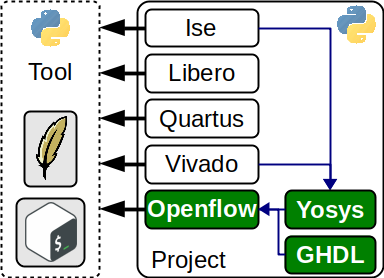
PyFPGA components¶
fpga/tool/template.tcl¶
Many (all?) FPGA development Tools provides a Tcl (Tool Command Language)
interface for the Bitstream generation.
This multi-vendor master Tcl was developed, where the different commands to
solve the complete workflow were encapsulated into procedures
(using the fpga_* prefix to avoid namespace conflicts).
Note
To add a new Tool, a case in the switch of each fpga_* must be
provided.
Note
This file is compliant with Tcl 8.4 because is the oldest used by a supported FPGA Tool (Xilinx ISE).
fpga/tool/<TOOL>.py¶
A base class (__init__.py) was developed to provides a uniform API to be
implemented for each supported Tool.
Also, validation of values is performed here.
Classes to supports each Tool (<TOOL>.py) implements the base class, ideally
setting a few variables.
Note
Transfer of the bitstream to a device is not always performed by a Tcl script, so special methods must be developed, following the proposed API.
fpga/project.py¶
This class implements the Application Programming Interface (API) which is employed to manage an FPGA project. It solves high-level things such as collect several files using glob, setting and use of a working/output directory and time measurement.
FAQ¶
How to deal with deprecated Tcl commands?¶
From Vivado 2019.1 to 2019.2, open_hw changed to open_hw_manager:
if { [ catch { open_hw_manager } ] } { open_hw }